Iran is currently facing a severe e-waste crisis. Research indicates that it is a country with a high usage of computer equipment, inevitably leading to a significant amount of e-waste generation. However, unsafe recycling practices, such as burning circuit boards and cables to extract copper, expose e-waste collectors to hazardous chemicals. The ash containing lead, mercury, and other heavy metals contaminates the soil and air.
According to the “Global E-waste Monitoring” report by the United Nations University, the world’s generation of electronic waste is rising five times faster than documented e-waste recycling. In Iran, only 20% of e-waste is properly recycled. The vast majority (80%) goes unrecorded and may be dumped, traded, or recycled under poor conditions.
Iran’s Actions in E-waste Management
It is regrettable that e-waste recycling has not been taken seriously in Iran. The public lacks awareness of the hazards of e-waste. But things have changed now. Have you noticed the guidelines on e-waste disposal formulated by the Ministry of Environment? For example, the Tehran Municipal Government has set up special recycling stations to collect recyclable materials, including e-waste. Undoubtedly, this is a positive step. The municipal authorities provide all recyclable waste in the city to third-party contractors. These contractors recycle e-waste and extract precious materials, not only protecting the environment but also making a profit by selling the extracted materials.

So, you may wonder, what is the standard process for collecting, disassembling, and recycling the metals contained in discarded electronic devices? That’s exactly what we’re going to talk about today, along with the essential machines involved.
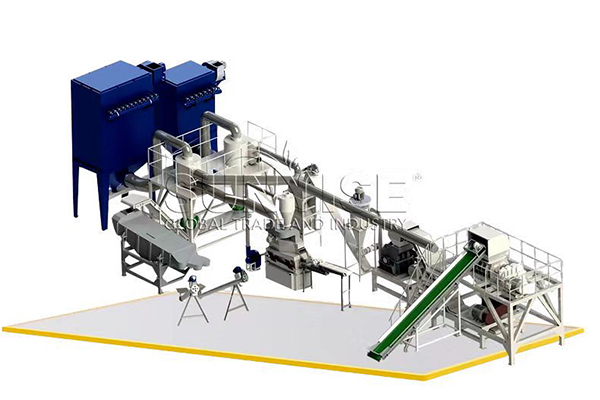
What’s the must-have machine for electronic waste recycling in Iran?
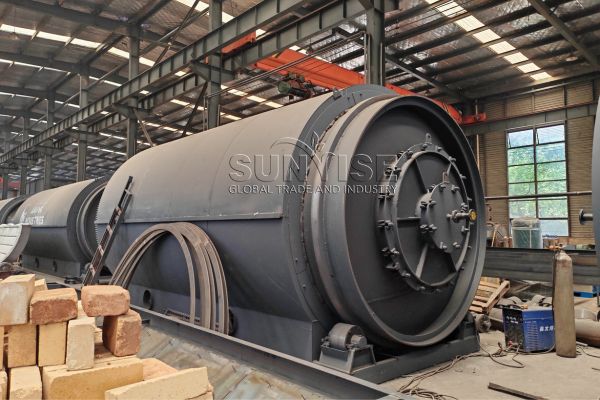
Let’s get straight to the point: the answer is shredder. In Iran, you can’t run the production line without an electronic waste recycling shredder. The main components of Iranian e-waste include discarded computers, mobile phones, televisions, and other household and industrial electronic products.
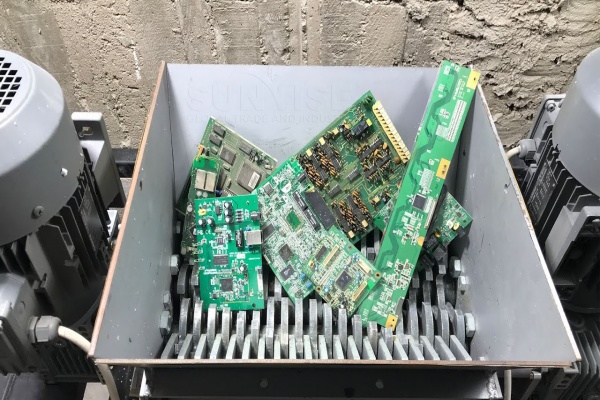

A shredder, like the YSX electronic scrap shredder, is crucial as it can break down large pieces of e-waste into smaller, more manageable fragments. It typically features a powerful motor, say around 30 – 50 kW, enabling it to handle various hard and bulky e-waste items. With sharp cutting blades and a robust design, it can efficiently cut through metal casings, plastic components, and circuit boards. This initial shredding process prepares the e-waste for further separation and extraction of valuable materials.
How to further improve e-waste recycling rate?
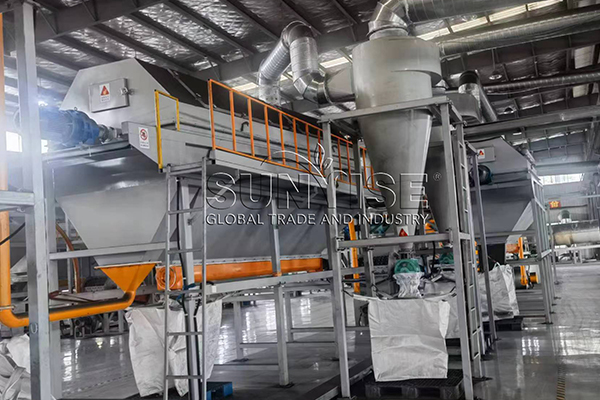
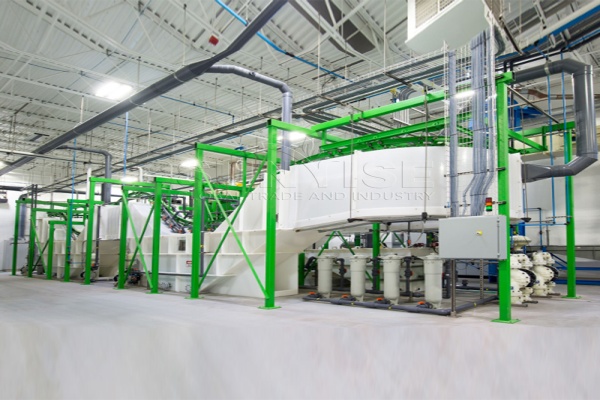
After tearing the large pieces of e-waste into small pieces, you now need to screen different materials such as copper, aluminum, silicon wafers, and so on. At this time, if you add a screening machine to your recycling production line, it will surely greatly increase your recycling rate. From the efficiency perspective, it can quickly distinguish materials of different sizes and properties, reducing the time-consuming manual sorting process. In terms of speed, it can handle a large volume of shredded e-waste continuously.
For example, a gravity separator machine can separate materials based on their density differences. If your budget allows, using screening equipment instead of manual screening is a choice you won’t regret. It not only speeds up the process but also improves the accuracy of material separation, ensuring that more valuable materials are recovered.
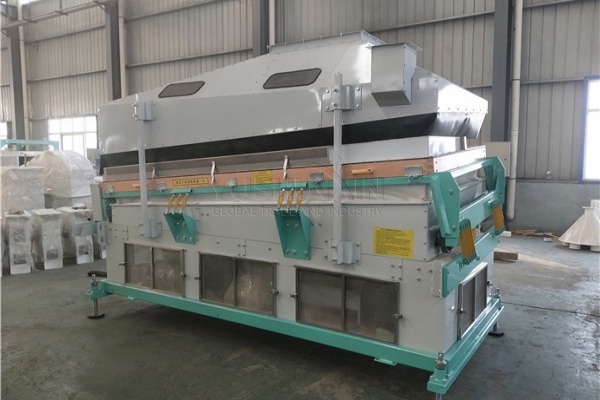

How to make the extracted material better quality?
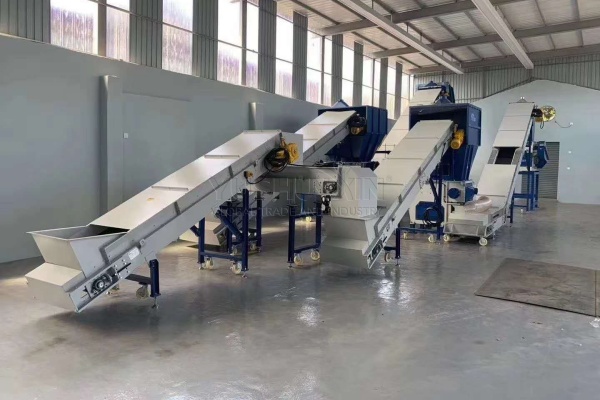

We all know that the finer the materials extracted from electronic waste, the higher the price they can be sold for. So what machine can help you further improve the quality of the materials extracted from electronic waste? The answer is the secondary shredder. Compared with the first coarse pulverization, the second pulverization is also called fine pulverization. The particle size after the second pulverization is significantly smaller. For instance, a secondary shredder with a finer cutting mechanism can further break down the already shredded e-waste into even smaller particles. This allows for better separation of different materials, especially when it comes to extracting precious metals. The products after secondary shredding have a more uniform particle size, which is beneficial for subsequent chemical extraction or other advanced processing methods. It helps to increase the purity of the extracted materials, making them more marketable.
Why choose us as your equipment supplier?
Contact Us