E-waste, or electronic waste, continues to pose a significant challenge globally due to rapid technological advancements and high turnover rates of electronic devices. Efficient e-waste management is crucial to mitigate environmental hazards and recover valuable materials. So now let’s talk about the solution for e waste management from these point of view.
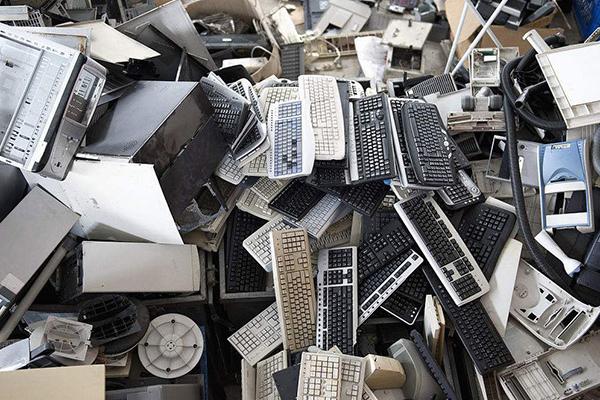


The Urgency of Effective E-Waste Management
E-waste contains hazardous substances such as mercury, lead, cadmium, and brominated flame retardants. If not properly managed, these substances can leach into soil and water, causing significant environmental and health risks. On the other hand, e-waste is a rich source of precious metals like gold, silver, and palladium, which can be recovered and reused, reducing the demand for virgin resources.
Key Components of an E-Waste Management Solution
Collection and Transportation
To streamline the e-waste management process, an efficient collection and transportation system is needed. This involves setting up designated collection points and using specialized vehicles for safe transport. Collection points should be conveniently located in urban and suburban areas to maximize consumer participation.
Environmental and Economic Advantages
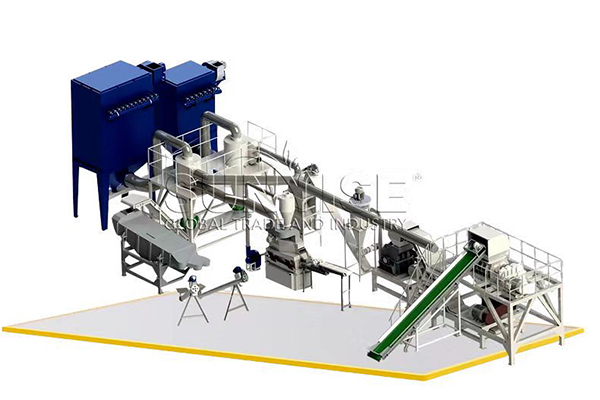
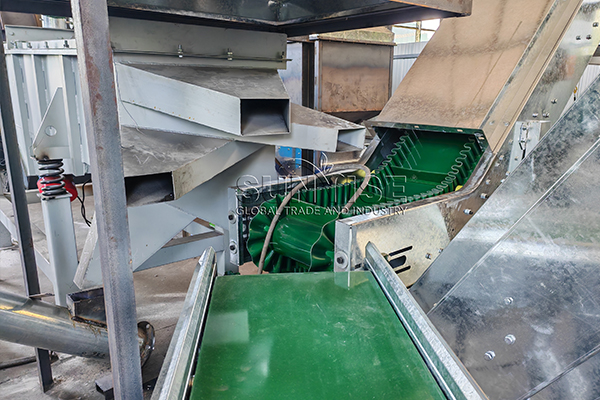
Initial Processing and Pre-sorting
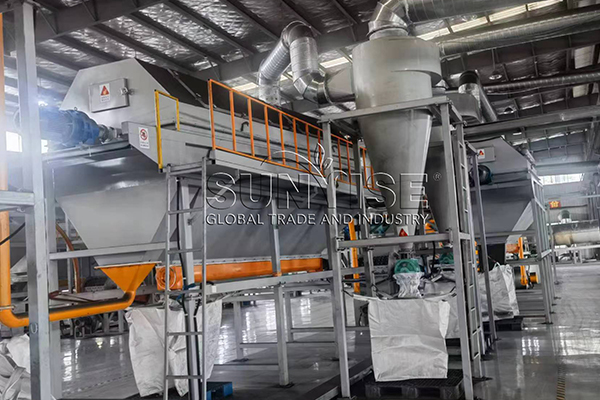
After collection, e-waste is transported to a processing facility where it undergoes pre-sorting. Here, items are categorized based on their type, size, and material composition. This initial step is crucial to optimize subsequent recycling processes.
Equipment Needed:
Conveyor Belts: For efficient movement of e-waste through different sorting stages.
Shredders: To reduce the size of larger items, making them easier to handle and process.


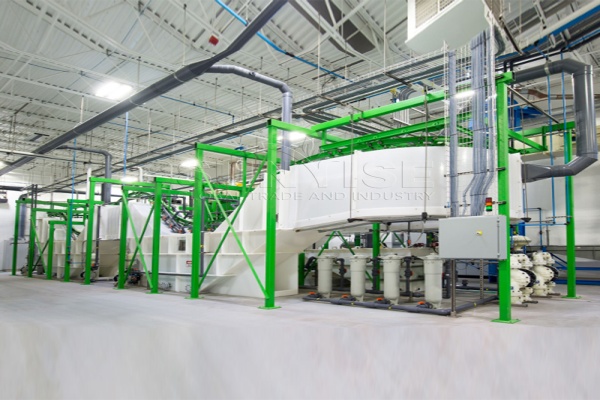
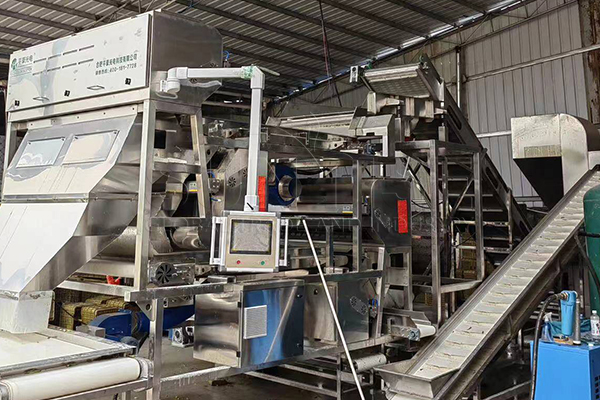
Mechanical Separation
Effective e-waste management relies heavily on advanced mechanical separation techniques. This phase includes the use of various equipment to segregate different materials based on their physical properties.
Equipment Needed:
Magnetic Separators: To extract ferrous metals from the waste stream.
Eddy Current Separators: For separating non-ferrous metals like aluminum and copper.
Density Separators: To separate materials based on their density, such as plastics from metals.

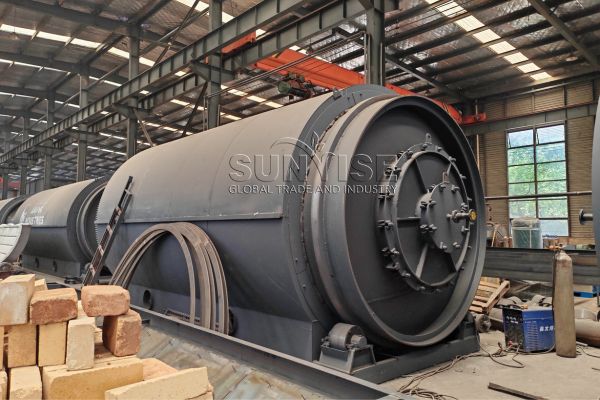
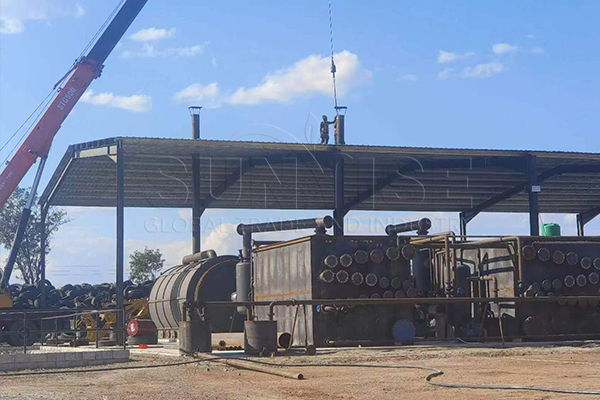
Chemical and Thermal Processing
For components that cannot be effectively separated through mechanical means, chemical and thermal processing methods are applied.
An effective e-waste management solution integrates advanced equipment and systematic approaches to address the growing challenge of electronic waste. By leveraging mechanical, chemical, and thermal processes, and ensuring regulatory compliance, valuable materials can be recovered, environmental harm minimized, and economic benefits realized. Continuous technological innovation and public engagement are key to the long-term success of e-waste management initiatives.
Contact Us