Peru is the world’s second largest copper producer and has rich mineral resources. Although its lithium deposits are not as abundant as those in the “Lithium Triangle” countries such as Bolivia, Chile and Argentina, there are still some lithium deposits in the southern border province of Puno. This offers a certain resource base to the lithium battery recycling industry, and we can combine the valuable metals in the recycled lithium batteries with the development of local mineral resources to achieve a coordinated development of the industrial chain.


With the advancement of the global automotive electrification transformation, the demand for lithium batteries continues to increase, which also indirectly promotes the demand for lithium battery recycling. As a country with mining resources, Peru has great potential for lithium battery recycling. The Peruvian government has expressed its desire to produce lithium batteries domestically and has begun to take action to promote the development of the industry. This provides policy support and investment opportunities for the lithium battery recycling industry, and Peru will surely further increase the demand for lithium battery recycling to meet the supply of raw materials.
So, how to start a lithium battery recycling business in Peru? On April 12, 2024, a customer from Peru inquired us about this project. Ya mere, anyị nyere eriri batrị 500kG / H LITETGE. N'okpuru ebe a bụ nkọwa nke mkparịta ụka anyị na onye ahịa a.
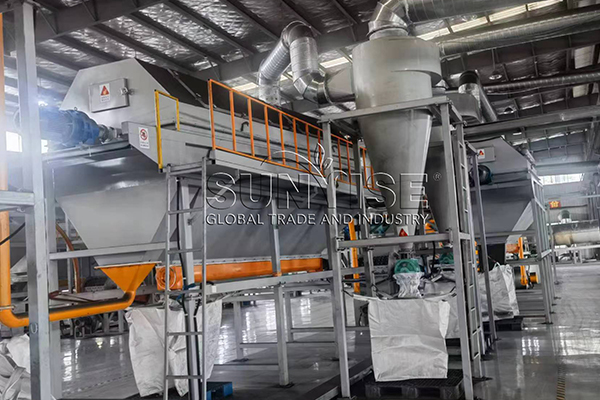
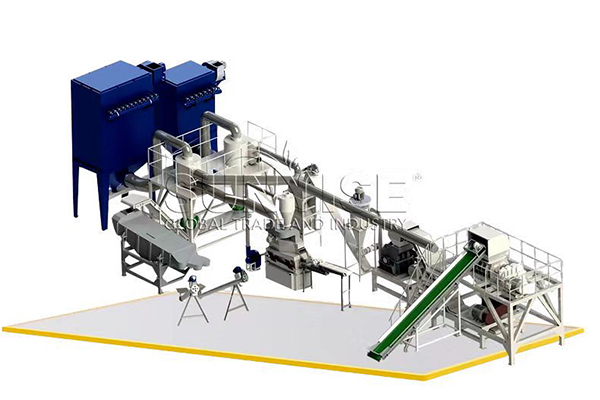
What machines are there in 500 kg/h Lithium Battery Recycling production line?
Onye ahịa Peruvian chọrọ ịma etu anyị si chepụta igwe maka ya. O kwuru na ya nwere olile anya na ikike nhazi nke usoro mmepụta bụ 500KG / H. Ya mere anyị mere ka usoro mmepụta nke dabara adaba maka ya maka ya.
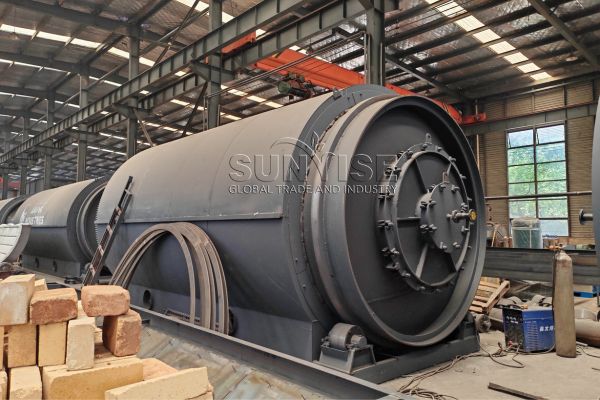
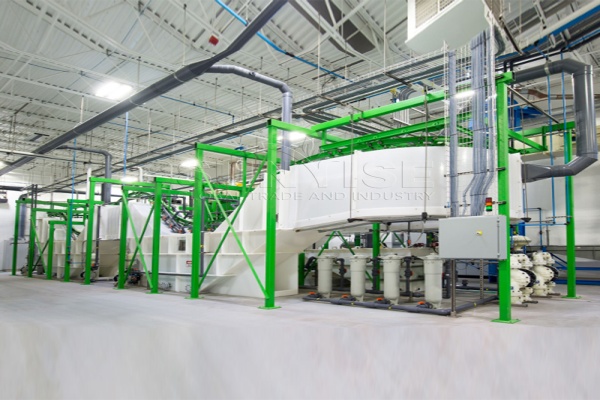
Oseihe nwaanyi 500 Ahịrị nke VG / H LITETCLE LEBERGE EGO NA-EGO EGO. Ọ gụnyere ngwaọrụ nri maka izipu batrị Lith na-egbu egbu; keadighi rarii igwe na-azọpịa Maka akwa a na-egbuji batrị lithium nwere ọkụ eletrik; Ngwaọrụ nkewa nke mbụ maka nyocha mbụ nke ntụ ntụ site na batrị Lithium; nke abuo magnetic kewapụ Iji wepu ihe mkpofu dịka shells na ihe ndọta; a hama isi maka ezigbo ihe; Ngwaọrụ nkewa nke na-emepụta akwụkwọ maka nyocha ojii na iche ma nkpuchi; ihe a grinder maka egweri ma gwepịa ihe mkpofu batrị; na ngwaọrụ nkewa dị iche iche maka ikechapụ ntụ ntụ, aluminom na ọla kọpa.
Na mgbakwunye, Enwere eriri eriri, Ihe na-emebi emebi, Ndị na-ahụ maka iche iche, diaphragm kewapụrụ, cyclone uzuzu uzuzu, August na-ebugharị, Ndị gbagwojuru agbagọ, Ndị na-eto eto ikuku, Play Plaliers na akụrụngwa ndị ọzọ.
What is the metal recovery rate of 500 kg/h Lithium Battery Recycling production line?
Ọ bụrụ na idozi usoro nke ahịrị dị ala, Recycled metal ga-enwe adịghị ọcha, na-emetụta ịdị ọcha ya. Makankeahu, Ahịa Peruvian jụrụ ajụjụ ọkachamara banyere ọnụego mgbake nke usoro nrụpụta.
Nke a bụ ezigbo ajụjụ. Linise batrị na-emepụta ihe mmepụta ọnụego mgbake nke ọla nke kariri 99.8% maka Nickel, pobe, na lithium. Mgbe ị ga-emechaa, Ọdịmma na usoro usoro ndị ọzọ, Enwere mbipụta nke ịdị ọcha ọla. Akụrụngwa anyị nwere ike nweta ọla ọcha nke kariri 95% Maka a gbakere na nickel, na ịdị ọcha nke 95% – 99% maka lithium. Aluminom, Enwere ike ijikọ ọla kọpa na ọganihu site na Lithium-Ion Carint, ihe niile dị oke ọnụ ahịa.
What’s the lifespan of 500 kg/h Lithium Battery Recycling production line?
Mgbe enwetara mkparịta ụka omimi, Ndị ahịa Peruvian na-eche na 500 Ahịrị batrị KG / h. Mgbe ahụ ọ chọrọ ịmata ogologo oge nke akara a na-eme.
N'ezie, ọtụtụ ndị ahịa emebere, na arụmọrụ dị elu, Ndụ ogologo ozi na nke kwụsiri ike. Enweghị nsogbu na iji usoro mmepụta maka 15-20 otutu, Ma enwere obere akụkụ.

How to ensure the safety of the entire production line?
Mgbe ị na-edozi ajụjụ ndị ọrụ na ndị ahịa Peruvian, Anyị bidoro ikwurita ajụjụ kachasị mkpa na nke kachasị mkpa: Bụ nchekwa nke eriri ahịrị dum?

A na-emegharị batrị na-emegharị batrị na-emegharị emegharị, nke a ga-ahọrọ dịka mkpa ndị ahịa si dị.
Ọmụmaatụ, Anyị na-eji Nchedo gas usoro ma webata nitrogen, Armon na gas ekike ọzọ n'oge ịzọpị iji mepụta gburugburu ebe obibi oxygen ka iji gbochie obere mgbakwasịtị ahụ na-eme ka ọkụ ma ọ bụ mgbawa. Ndị ahịa nwekwara ike ịhọrọ akụrụngwa eji ihe ọkụ na ihe mgbawa. Anyị emeela nke ọma n'ime ngwa ọrụ iji hụ na ọ nwere ike igbochi ọkụ ahụ site na ịgbasa na ọnọdụ nke ọnọdụ na-adịghị mma.
Maka nchekwa nke ndị ọrụ, Na mgbakwunye na usoro a kpọtụrụ aha na usoro ihe mgbochi, Anyị ga-akwadebe akụrụngwa ahụ nsochi ngwaọrụ, bọtịnụ mberede na-akwụsị, wdg. Dos, Anyị nwere ike ịkwụsị ngwa ahụ n'oge ihe egwu iji chebe nchekwa nke ndị ọrụ. Na mgbakwunye, Mgbe nnyefe na nwụnye, Ọwụwa anyanwụ ga-enye Ọzụzụ ọkachamara Maka ndị na-emepụta ihe na-arụ ọrụ iji mara usoro arụmọrụ na usoro nchekwa nke akụrụngwa, Kpamkpam nọgide na usoro arụmọrụ, and ensure the safety of personnel during the operation of the equipment.
In short, the 500 kg/h lithium battery recycling line we designed for our Peruvian customer has a clear process flow and rich equipment composition. Multiple equipment work together to achieve efficient extraction of metals from waste lithium batteries through a series of process steps such as crushing, sorting, pyrolysis, and grinding.
Does this Peruvian case study give you some inspiration in lithium battery recycling? Na mgbakwunye, if you also need any other e-waste recycling machine (solar panel recycling na circuit board recycling), or tire pyrolysis machine, please contact us.
Kpọtụrụ anyị